Guide to Choosing the Right Transformer Oil for Your Needs
Introduction to Transformer Oils
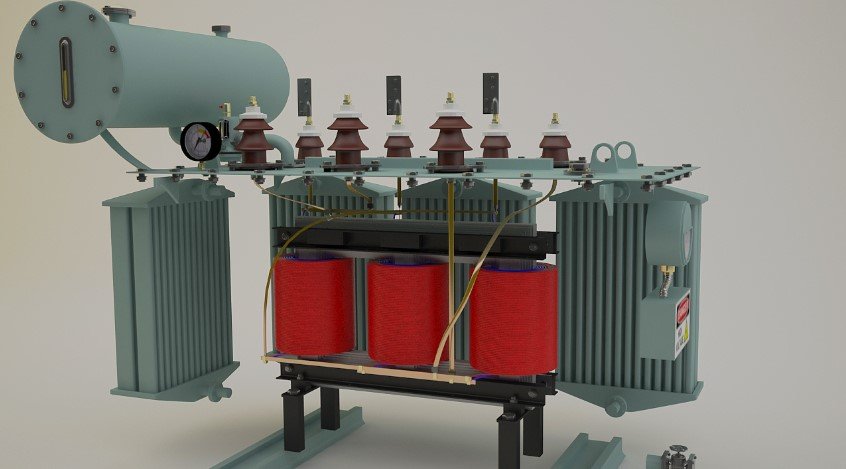
What is Transformer Oil?
Different Types of Transformer Oil
There are several types of transformer oils available today. These oils can be categorized based on their chemical composition:
Mineral Oil-based Transformer Oils
- Mineral oils are the most commonly used in transformers. They are natural oils derived from crude oil through refining. Mineral oils are low-cost, widely available, and have reliable insulating properties. However, they do have limitations in terms of thermal stability, flammability, and environmental impact.
Synthetic Oils
- Silicone-based transformer oils are synthetic oils that offer excellent performance, especially in high-temperature applications. These oils have superior thermal stability and can operate over a wider range of temperatures compared to mineral oils.
- Esters (natural or synthetic) are biodegradable oils, providing an eco-friendly alternative to mineral oil. While more expensive, esters offer high-performance characteristics and are preferred in areas that require environmental sensitivity and fire safety.
Each of these oils has its advantages and limitations, so it’s crucial to choose the right type for your specific application.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Transformer Oil
The choice of transformer oil depends on several critical factors that influence performance, reliability, and safety:
Temperature Tolerance: Transformer oils should be able to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from extremely hot to very cold. Synthetic oils generally offer better temperature tolerance than mineral oils.
Viscosity: Oil viscosity impacts the efficiency of heat dissipation and the flow of oil through the transformer. Low-viscosity oils can move more easily through the transformer, ensuring better heat management. Choose oils with appropriate viscosity that aligns with the operating conditions of your transformer.
Dielectric Properties: The oil must have good electrical insulating properties. Oils with higher breakdown voltage (the voltage at which the oil will fail to insulate) are preferred in high-voltage transformers.
Fire Resistance: Oil should have high fire-resistance to reduce the risk of fire or explosions in case of overheating or faults. Mineral oils are flammable, whereas ester-based oils have better fire-resistance properties.
Environmental Impact: Consider the long-term environmental consequences of the oil. Synthetic oils are more environmentally friendly and biodegradable, while mineral oils can cause more damage in the event of leaks or spills.
Transformer Oil Quality and Standards
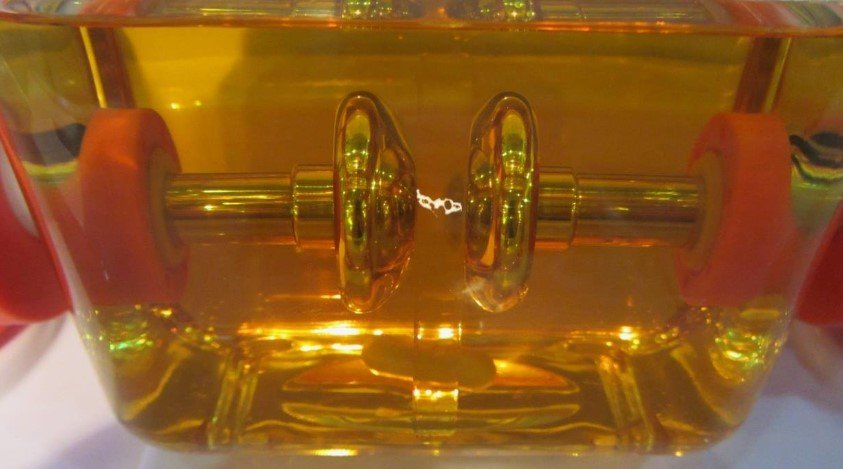

It’s important to select transformer oil that meets the established industry standards to guarantee optimal performance. These standards ensure that the oil is free from contaminants, has the right chemical composition, and performs reliably across a range of operational environments.
- IEC 60296: This is the International Electrotechnical Commission’s standard for mineral insulating oils, which defines the technical properties required for transformer oils.
- ASTM D3487: This standard specifies the requirements for mineral oils used in electric transformers, focusing on chemical properties, oxidation stability, and insulating performance.
- IS 335: The Indian Standard for transformer oils, specifying physical and chemical requirements for oils used in transformers.
Using oil that meets these standards can help ensure the safety and efficiency of your transformer, prolonging its service life.
Synthetic Oils vs. Mineral Oils: Which is Better?
While mineral oils are widely used due to their affordability and availability, synthetic oils are becoming more popular due to their superior performance in specific applications.
Synthetic oils (including silicone and ester oils) generally offer superior thermal stability, electrical insulation, and fire-resistance properties. These oils can operate in extreme temperature environments where mineral oils might degrade more quickly.
Mineral oils are a more cost-effective choice but may lack the advanced properties of synthetic oils. They are better suited for transformers that operate under moderate conditions.
Consider the operational environment, regulatory requirements, and costs when making your decision. Synthetic oils may cost more upfront but could offer long-term savings due to their enhanced properties and longer life.
Environmental Considerations in Transformer Oil Selection
Environmental impact is becoming an increasingly important factor in selecting transformer oil. Synthetic oils, particularly ester-based oils, are biodegradable, reducing the ecological footprint of transformer operations.
In areas where spills or leaks are more likely, biodegradable and eco-friendly oils are a smart choice. They have lower environmental hazards and can be disposed of more easily. Additionally, synthetic oils like vegetable-based esters not only provide eco-friendly benefits but are also less prone to degradation over time, offering an environmentally safe solution without compromising transformer efficiency.
Impact of Transformer Oil on Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is critical in the selection of transformer oil. The oil helps prevent electrical discharge and protects against electrical short circuits.
Transformer oil serves as an insulating medium, reducing the risk of faults. It forms a barrier between the electrical components, which helps keep them insulated and reduces the chances of internal damage.
Additionally, transformer oil is crucial for cooling the transformer. Oil absorbs the heat produced during normal transformer operations and transports it through the tank to keep the transformer within optimal operating temperatures. This ensures that the transformer doesn’t overheat, which could otherwise lead to a dangerous failure.
How to Properly Maintain Transformer Oil
Regular maintenance of transformer oil is necessary to maintain its performance. Transformer oil can degrade over time due to factors such as oxidation, temperature, and contaminants. Here’s how to maintain it:
Regular Testing: Perform routine oil tests to assess moisture content, acidity, and electrical conductivity. These tests help detect early signs of oil degradation or contamination.
Filtration: Use filtration to remove impurities and moisture that accumulate in the oil over time. This helps maintain the insulating and cooling properties of the oil.
Reconditioning: When the oil shows signs of aging, reconditioning techniques such as vacuum filtration and degassing can restore its effectiveness.
Oil Replacement: If the oil becomes too degraded, replacement might be necessary. Consider oil analysis to determine when the oil has reached the end of its useful life.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Choosing the right transformer oil is not a decision to take lightly. Understanding your transformer’s requirements, including operating temperature range, dielectric properties, fire resistance, and environmental impact, is key to selecting the best oil for your needs.
While mineral oils remain the standard in many applications, synthetic oils offer distinct advantages in extreme conditions. Always check for compliance with industry standards, and consider the environmental footprint of the oil type you choose.
By taking a proactive approach to oil selection and maintenance, you ensure that your transformers remain efficient, safe, and operational for many years. Consult oil specifications, industry standards, and professional advice before finalizing your choice to guarantee that your transformer is optimized for longevity and performance.